
V) requirements of the process or product in terms of its design for reliability, safety, quality, Iv) the priority factors which may contribute to an failure event,

Iii) the potential exposure of the process to single or multiply human errors, Ii) potential process design or operation weaknesses, I) the potential causes of failure events which could arise, Why would you perform a Fault Tree Analysis? The FTA analysis provides a very comprehensive quantitative and qualitative review of a process (or product) allowing very structure risk analysis to be applied.įTA analysis forces a logical approach to failure analysis.įTA forces an analysis from the top down, which can often be combined with say an FMEA bottom up approach to failure assessment to provide differing yet complimentary approaches to failure event analysis. You gain a very comprehensive knowledge of a process or product through the FTA process. This then allows for simple overall risk estimation of the likelihood of the top level failure event arising.īy completing a fault tree, you build a diagram of the different relationships that are required for a failure event to arise. Once an FTA tree is defined, then a probability of event occurrence can be attached to each event. Risk Estimation using Fault Tree Analysis. Iv) Standard practice is that the gates (And, Or) are not directly connected together, but rather failure causes are linked via gates. Iii) The causes listed in an FTA, may arise from user errors, machine failures, environmental factors, or any form of unexpected or undesired event. Ii) An FTA may be quantitative (specific risk related numbers) or qualitative (pass / fail analysis). I) An FTA is routinely defined in the form of a tree diagram of causes. What is Fault Tree Analysis – standard format? You continue the process of listing out potential causes for each failure event until you work down to the potential root cause. There are two logic gates an “And” and an “Or” gate, which are used to show the relationship between the causes leading to a failure.įor example an “And” is shown on an FTA tree, where two or more causes are required to happen simultaneously in order for the failure event to arise.Īn “Or” gate is shown on the FTA tree, where the failure event will arise when either or any of the failure causes arise. We can now start to construct the fault tree, starting at the highest potential impact failure event and working down the FTA tree, listing out the possible causes leading to the event. We can then implement modifications to the process or product, to reduce the probability of cause failure and by implication of final event failure. We can then calculate the probability for the failure event itself. Then we calculate the probability of the causes of failure. When constructing an FTA diagram, we start by asking the questions:Ī) What is the potential failure event we want to understand?ī) What are the most probable causes leading to this failure event?Ĭ) Are there a combination of causes which could lead to the failure event?Īs we identify potential failure causes, we show on the FTA tree. Information, Training & current Best Practice > The top of the tree is the undesired event, below this are the potential causes leading up to the undesired event.Ĭontinuous improvement utilizing Analytical Techniques.

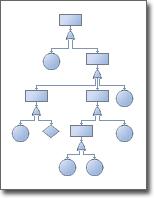
In an FTA analysis, we build a visual failure analysis tree diagram. This may then lead onto the final undesired outcome of the pacemaker not working.
Then ask the question, if the battery fails, what would be the effect. Under an FMEA analysis, we would look at a potential failure within a component, e.g. We would work backwards to (say) the battery potentially failing. We would then seek to understand the causes leading up to this undesired event. Under a Fault Tree Analysis, the failure event may be that the pacemaker stops. What this means is that you are taking a top level view of a process or a product, identifying a potential failure or undesired event which could arise and trying to understand the potential causes of the failure event.įault Tree Analysis (FTA) is used to investigate potential failures, the causes of these failings, and seeks to quantify the impact of the failings on a product or process.įault Tree Analysis is opposite to an FMEA (Failure Mode Effects Analysis) in that FTA seeks to identify potential failure modes by taking a top down approach, whereas an FMEA takes a bottom up approach.įor example consider a “heart pacemaker”.
CAFTA FAULT TREE TOOL IMAGES HOW TO
What is Fault Tree Analysis? How to implement FTA Analysis?Fault Tree Analysis is a top down approach to problem solving.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
